With increasing reliance on technology to streamline hospital’s tasks, improve patient care, and to manage huge amounts of patient sensitive information, practices should prioritize healthcare security compliance more than even before.
Healthcare compliance is a broad term where practices take massive efforts to ensure that they are meeting the necessary protocols, procedures, processes, measures, and staffing to avoid any fraudulent activities and misuse within their operations. Its primary goal is to ensure that organizations fulfill the legal, professional, and ethical obligations imposed by various healthcare regulations.
In this blog, we will look into the problems that practices struggle with lacking healthcare security compliance, potential risks involved, and the solutions to tackle those challenges.
Introduction: The Importance of Healthcare Compliance
Practices should manage patient’s sensitive data including patient demographics, medical histories, insurance data, and financial records. Based on the 2023 Data Breach Report from Ponemon Institute, the healthcare institutions got the highest average cost per breach which is around $10.93 million. (add in intro and merge and change the no.)
With this rising healthcare patient data breaches, practices should urge to set up robust healthcare security compliance measures to safeguard sensitive patient data. The necessity for healthcare compliance is critical with the growing complexity of regulations. That is why healthcare organizations are required to meet various requirements and frameworks, making it imperative to adopt a comprehensive approach to security compliance.
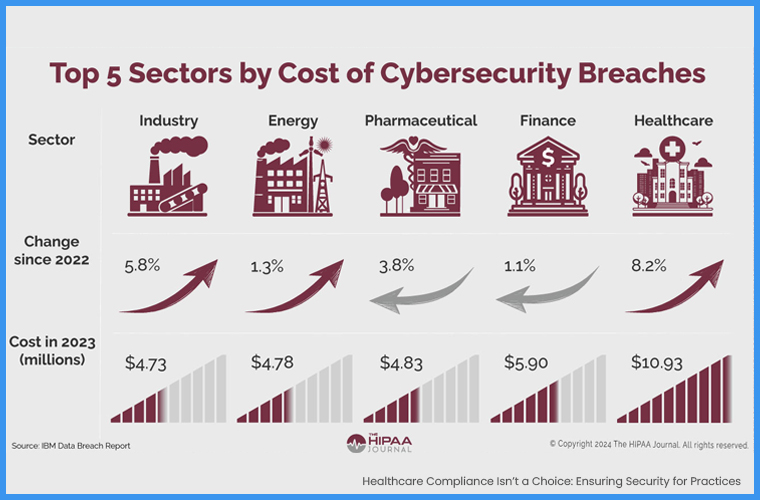
Source: IBM: Average Cost of a Healthcare Data Breach Increases to Almost $11 Million By Steve Alder on Jul 24, 2023 (The HIPAA Journal)
Problems Faced by Healthcare Practices Without Security Compliance
Practices that neglect to prioritize healthcare security compliance often face significant problems that can negatively impact their overall revenue and patient relationships. Some of the problems that they face include: – (add more conversational tone (I, me, thoughts) ( add image source for statistics)
Cyberattacks & Privacy Breach in Healthcare
In 2023, healthcare providers have reported to the Department of Health and Human Services Office for Civil Rights about the theft/unlawful exposure of 133 million data records. As such an incident occurred in healthcare, it ended with significant financial and reputational losses through compliance penalties and lawsuits. However, the issue still stands: why are these high numbers?
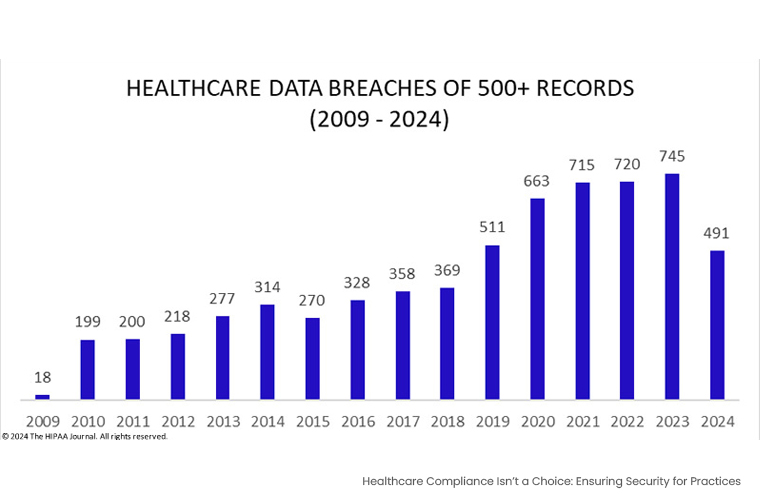
Source: Healthcare Data Breach Statistics By Steve Alder on Sep 24, 2024 The HIPAA Journal
| Rank | Name of Covered Entity | Year | Covered Entity Type | Individuals Affected | Type of Breach |
| 1 | Anthem Inc. | 2015 | Health Plan | 78,800,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 2 | American Medical Collection Agency | 2019 | Business Associate | 26,059,725 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 3 | Welltok, Inc. | 2023 | Business Associate | 14,762,475 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 4 | Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, Inc. | 2024 | Health Plan | 13,400,000 | Unauthorized Access/Disclosure |
| 5 | Optum360, LLC | 2019 | Business Associate | 11,500,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 6 | HCA Healthcare | 2023 | Business Associate | 11,270,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 7 | Premera Blue Cross | 2015 | Health Plan | 11,000,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 8 | Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings dba LabCorp | 2019 | Healthcare Provider | 10,251,784 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 9 | Excellus Health Plan, Inc. | 2015 | Health Plan | 9,358,891 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 10 | Maximus, Inc. | 2023 | Business Associate | 9,179,226 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 11 | Perry Johnson & Associates, Inc., which does business as PJ&A | 2023 | Business Associate | 8,952,212 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 12 | Managed Care of North America (MCNA) | 2023 | Business Associate | 8,861,076 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 13 | Community Health Systems Professional Services Corporations | 2014 | Healthcare Provider | 6,121,158 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 14 | PharMerica Corporation | 2023 | Healthcare Provider | 5,815,591 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 15 | Science Applications International Corporation (SA | 2011 | Business Associate | 4,900,000 | Loss |
| 16 | HealthEC LLC | 2023 | Business Associate | 4,656,293 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 17 | Community Health Systems Professional Services Corporation | 2014 | Business Associate | 4,500,000 | Theft |
| 18 | University of California, Los Angeles Health | 2015 | Healthcare Provider | 4,500,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 19 | HealthEquity, Inc. | 2024 | Business Associate | 4,300,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 20 | Reventics, LLC | 2023 | Business Associate | 4,212,823 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 21 | 20/20 Eye Care Network, Inc | 2021 | Business Associate | 4,142,440 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 22 | OneTouchPoint, Inc. | 2022 | Business Associate | 4,112,892 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 23 | Colorado Department of Health Care Policy & Financing | 2023 | Health Plan | 4,091,794 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 24 | Advocate Health and Hospitals Corporation, d/b/a Advocate Medical Group | 2013 | Healthcare Provider | 4,029,530 | Theft |
| 25 | Concentra Health Services, Inc. | 2024 | Healthcare Provider | 3,998,163 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 26 | Banner Health | 2016 | Healthcare Provider | 3,620,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 27 | Medical Informatics Engineering | 2015 | Business Associate | 3,500,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 28 | Florida Healthy Kids Corporation | 2021 | Health Plan | 3,500,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 29 | Newkirk Products, Inc. | 2016 | Business Associate | 3,466,120 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 30 | Regal Medical Group, Lakeside Medical Organization, ADOC Acquisition, & Greater Covina Medical Group | 2023 | Healthcare Provider | 3,388,856 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 31 | Trinity Health | 2020 | Business Associate | 3,320,726 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 32 | CareSource | 2023 | Business Associate | 3,180,537 | Unauthorized Access/Disclosure |
| 33 | Cerebral, Inc | 2023 | Business Associate | 3,179,835 | Unauthorized Access/Disclosure |
| 34 | Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services | 2024 | Health Plan | 3,112,815 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 35 | NationsBenefits Holdings, LLC | 2023 | Business Associate | 3,037,303 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 36 | Advocate Aurora Health | 2022 | Healthcare Provider | 3,000,000 | Unauthorized Access/Disclosure |
| 37 | Harvard Pilgrim Health Care | 2023 | Health Plan | 2,967,396 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 38 | Dominion Dental Services, Inc., Dominion National Insurance Company, and Dominion Dental Services USA, Inc. | 2019 | Health Plan | 2,964,778 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 39 | Lincare Holdings Inc. | 2021 | Healthcare Provider | 2,918,444 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 40 | Acadian Ambulance Service | 2024 | Healthcare Provider | 2,896,985 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 41 | Navvis & Company, LLC | 2023 | Business Associate | 2,824,726 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 42 | A&A Services d/b/a Sav-Rx | 2024 | Business Associate | 2,812,336 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 43 | ESO Solutions, Inc. | 2023 | Business Associate | 2,700,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 44 | Connexin Software, Inc. | 2022 | Business Associate | 2,675,934 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 45 | AccuDoc Solutions, Inc. | 2018 | Business Associate | 2,652,537 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 46 | NEC Networks, LLC d/b/a CaptureRx | 2021 | Business Associate | 2,600,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 47 | Smile Brands, Inc. | 2021 | Business Associate | 2,592,494 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 48 | WebTPA Employer Services, LLC (“WebTPA”) | 2024 | Business Associate | 2,518,533 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 49 | Enzo Clinical Labs, Inc. | 2023 | Healthcare Provider | 2,470,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 50 | Florida Health Sciences Center, Inc. dba Tampa General Hospital | 2023 | Healthcare Provider | 2,430,920 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 51 | Forefront Dermatology, S.C. | 2021 | Healthcare Provider | 2,413,553 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 52 | INTEGRIS Health | 2024 | Healthcare Provider | 2,385,646 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 53 | Shields Health Care Group, Inc. | 2022 | Business Associate | 2,380,483 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 54 | Postmeds, Inc. | 2023 | Healthcare Provider | 2,364,359 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 55 | Medical Management Resource Group, L.L.C. | 2024 | Business Associate | 2,350,236 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 56 | Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services | 2023 | Health Plan | 2,342,357 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 57 | 21st Century Oncology | 2016 | Healthcare Provider | 2,213,597 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 58 | Berry, Dunn, McNeil & Parker, LLC | 2023 | Business Associate | 2,068,426 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 59 | Xerox State Healthcare, LLC | 2014 | Business Associate | 2,000,000 | Unauthorized Access/Disclosure |
| 60 | Arietis Health, LLC | 2023 | Business Associate | 1,975,066 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 61 | Great Expressions Dental Centers | 2023 | Healthcare Provider | 1,925,397 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 62 | Professional Finance Company, Inc. | 2022 | Business Associate | 1,918,941 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 63 | IBM | 2011 | Business Associate | 1,900,000 | Unknown |
| 64 | Apria Healthcare LLC | 2022 | Healthcare Provider | 1,868,831 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 65 | Pension Benefit Information, LLC | 2023 | Business Associate | 1,866,694 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 66 | Performance Health Technology | 2023 | Business Associate | 1,752,076 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 67 | Clinical Pathology Laboratories, Inc. | 2019 | Healthcare Provider | 1,733,836 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 68 | Dental Care Alliance, LLC | 2020 | Business Associate | 1,723,375 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 69 | GRM Information Management Services | 2011 | Business Associate | 1,700,000 | Theft |
| 70 | Baptist Medical Center | 2022 | Healthcare Provider | 1,608,549 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 71 | Inmediata Health Group, Corp. | 2019 | Healthcare Clearing House | 1,565,338 | Unauthorized Access/Disclosure |
| 72 | Eskenazi Health | 2021 | Healthcare Provider | 1,515,918 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 73 | Community Health Network, Inc. as an Affiliated Covered Entity | 2022 | Healthcare Provider | 1,500,000 | Unauthorized Access/Disclosure |
| 74 | The Kroger Co. | 2021 | Healthcare Provider | 1,474,284 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 75 | EyeMed Vision Care LLC | 2020 | Business Associate | 1,474,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 76 | MEDNAX Services, Inc. | 2020 | Business Associate | 1,442,997 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 77 | Iowa Health System d/b/a UnityPoint Health | 2018 | Business Associate | 1,421,107 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 78 | St. Joseph’s/Candler Health System, Inc. | 2021 | Healthcare Provider | 1,400,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 79 | Novant Health Inc. | 2022 | Business Associate | 1,362,296 | Unauthorized Access/Disclosure |
| 80 | North Broward Hospital District d/b/a Broward Health | 2022 | Healthcare Provider | 1,351,431 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 81 | Prospect Medical Holdings, Inc. | 2023 | Business Associate | 1,309,096 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 82 | University Medical Center of Southern Nevada | 2021 | Healthcare Provider | 1,300,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 83 | CareFirst Blue Cross Blue Shield | 2015 | Health Plan | 1,300,000 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 84 | Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center | 2022 | Healthcare Provider | 1,290,104 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 85 | Geisinger | 2024 | Healthcare Provider | 1,276,026 | Unauthorized Access/Disclosure |
| 86 | American Anesthesiology, Inc. | 2021 | Healthcare Provider | 1,269,074 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 87 | Scripps Health | 2021 | Healthcare Provider | 1,267,639 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 88 | Employees Retirement System of Texas | 2018 | Health Plan | 1,248,263 | Unauthorized Access/Disclosure |
| 89 | INTEGRIS Health, Inc. | 2019 | Healthcare Provider | 1,245,218 | Loss |
| 90 | Virginia Department of Medical Assistance Services | 2023 | Health Plan | 1,229,333 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 91 | PurFoods, LLC | 2023 | Healthcare Provider | 1,229,333 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 92 | UNM Health | 2021 | Healthcare Provider | 1,228,093 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 93 | Nuance Communications, Inc. | 2023 | Business Associate | 1,225,054 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 94 | AvMed, Inc. | 2010 | Health Plan | 1,220,000 | Theft |
| 95 | Professional Business Systems, Inc., d/b/a Practicefirst Medical Management Solutions and PBS Medcode Corp., | 2021 | Business Associate | 1,210,688 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 96 | Doctors’ Center Hospital | 2022 | Healthcare Provider | 1,195,220 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 97 | Baesman Group, Inc. | 2023 | Business Associate | 1,170,094 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 98 | Presbyterian Healthcare Services | 2019 | Healthcare Provider | 1,120,629 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 99 | JDC Healthcare Management LLC | 2021 | Healthcare Provider | 1,077,635 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 100 | Montana Department of Public Health & Human Services | 2014 | Health Plan | 1,062,509 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 101 | The Nemours Foundation | 2011 | Healthcare Provider | 1,055,489 | Loss |
| 102 | Inova Health System | 2020 | Healthcare Provider | 1,045,270 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 103 | Wolverine Solutions Group | 2018 | Business Associate | 1,024,731 | Hacking/IT Incident |
| 104 | BlueCross BlueShield of Tennessee, Inc. | 2010 | Health Plan | 1,023,209 | Theft |
| 105 | Magellan Health Inc. | 2020 | Health Plan | 1,013,956 | Hacking/IT Incident |
Source: Healthcare Data Breach Statistics (The HIPAA Journal)
Firstly, healthcare institutions are major targets for cyberattacks, considering the fact of valuable patient information in the black market. Secondly, the data protection strategies often do not meet the required standards.
The lack of effective healthcare cybersecurity compliance protocols leaves healthcare practices exposed to various cyber threats, including phishing attacks, ransomware, and data exfiltration.
Loss of Patient Trust
Patient trust is important for the success of any practices. Even a single patient data breach may cause a loss of confidence among your patients, ultimately breaking your trust and decreasing patient retention. Patients would even consider switching providers if their data were comprised.
When patients no longer trust your practice to protect their sensitive data, it may affect your reputation and financial stability. Ultimately, your patients are less likely to recommend your practice to others, which can affect referrals and overall growth, further compounding reputational harm.
Financial Penalties and Legal Liabilities
Non-compliance with healthcare industry regulations can lead to severe financial penalties. For instance, the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) at the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) enforces HIPAA compliance and can impose severe fines along with huge penalties. So, what are the HIPAA violations fines?
- For unintentional healthcare data security privacy and compliance violations, the OCR charges fine from $100 to $50,000 along with annual penalty of $1,500,000
- For healthcare data security privacy and compliance violations due to reasonable cause, the penalty varies from $1,379 to $68,928, along with an annual cap of $2,067,813.
The financial burden of non-compliance penalties is further exacerbated by legal liabilities, as affected patients may pursue lawsuits against organizations that fail to protect their data adequately.
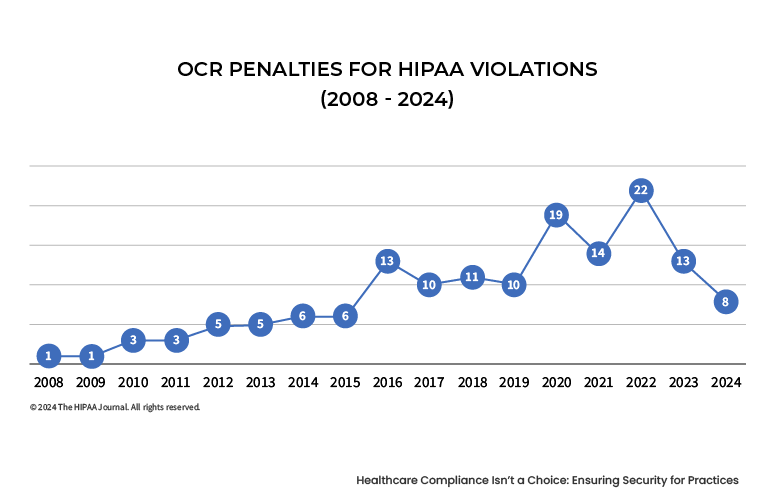
Source: OCR Penalties for HIPAA Violations Sep 24, 2024 - The HIPAA Journal
Healthcare Workflow Disruption:
Soon after a data breach in any healthcare organization, there will be a need to shut down temporarily resulting in workflow disruptions and reduced productivity. Based on security concerns, any organization has to go through such a temporary shutdown.
However, some healthcare practices can be incapacitated for many months, and they may take a longer downtime to come out from a ransomware attack.
Difficulty in Obtaining Insurance Coverage:
With increasing cyberattacks and ransomware threats, getting cybersecurity insurance has become a challenge for independent medical practice lacking proper cybersecurity compliance protocols. Insurers often ask for the firms to stick to the security standards and regulations before providing you with the required insurance policies.
Non-compliance may end with charging higher premiums or even coverage denials. Finally, healthcare practices are vulnerable to financial losses in the event of data breach.
Potential Risks of Ignoring Healthcare Compliance:
Ignoring healthcare security compliance in the healthcare industry may pose a range of risks and consequences. (add all these bullet points and give a brief of topics covered beneath)
Increased Vulnerability to Cyberattacks
Without compliance measures in place, healthcare organizations are more susceptible to data threats and cyberattacks. Cybercriminals are adept at exploiting vulnerabilities in outdated technology, unpatched software, and inadequate access controls.
Did you know that 83% of healthcare organizations experienced a catastrophic data breach of more than once in just two years?
Yes, IBM has a clear report, and the surprising fact is that only 17% of data breaches were first-time attacks. This enforces the need to protect sensitive patient information using healthcare compliance standards and encryption protocols.
Damage to Reputation: Regulatory Fines
Legal Ramifications: Breaking Boundaries
Data breaches in healthcare organizations can lead to serious consequences including class action lawsuits and legal ramifications. Did you know that on July 19, 2024, Change Healthcare filed a breach report with OCR about the ransomware attack ended with the breach of PHI? It was a massive attack on PHI leading to 500 affected individuals to be an approximate number. (use HHS remove Change Healthcare)
This catastrophic data breach led to a federal judicial panel ruling to consolidate nearly 50 lawsuits against Change Healthcare in Minnesota in 2024. Legal battles can be lengthy and costly, diverting resources away from patient care and negatively impacting organizational morale. but(as per report over US department of healthcare)
Comprising Patient Safety: Decreased Engagement
Patient Safety must always be the top priority within any healthcare setting be it an independent medical practice or multilocality medical practice. Failure to adhere to important protocols puts your patients at unwanted risks. Moreover, patients are increasingly concerned about their privacy and security.
In fact, a survey by Accenture found that 64% of patients would consider changing their providers due to data security concerns. Ignoring healthcare security compliance can lead to decreased patient engagement and satisfaction, ultimately affecting the quality of care provided.
Loss of Competitive Advantage
In an increasingly competitive healthcare landscape, organizations that fail to prioritize healthcare compliance may end up losing their competitive edge. Patients are more likely to choose providers that demonstrate strong security practices and a commitment to safeguarding their information. Non-compliance can result in reduced patient referrals and a decline in market share. ( add change healthcare data breach and its negative impact on their trust/reputation)
Solution: Why Compliance Matters & Why Practices Must Prioritize HIPAA, HITRUST, SOC 2, and GDPR?
CERTIFY Health is a leading practice management platform that recognizes the significance of staying compliant with local, state and federal US regulations. Our platform meets the highest industry standards, that is certified with
- HIPAA Compliance
- HITRUST
- SOC 2 TYPE 2 COMPLIANCE
- GDPR
Meeting all the above healthcare compliances ensures that your practices are free from the above problems and risk factors to handle patient data with the greatest care and security. By Integrating with HIPAA, HITRUST, SOC 2 Type II, and GDPR solutions, your practices can focus on improving your patient experience and revenue collections without worrying about data breaches.
Before discussing CERTIFY Health and its need for practices to integrate, we will have a detailed discussion about each of these healthcare compliances for better understanding. (what the hospital industry would need to consider help their care industry into – add the point most of the hospitals are compliant with HIPAA, but few are in compliance with HITRUST, SOC 2 – what people oversee is GDPR in US market and majorly oversee someone who is not compliant with all of these 4)
A Brief Idea About HIPAA, HITRUST, GDPR, and SOC 2 Compliances:
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act):

HIPAA is a federal U.S. law enforced in 1996 to protect your patient’s sensitive information. HIPAA compliance sets certain standards to protect an individual’s medical information along with other personal health records.
The regulatory compliance ensures that health systems, provider groups and other specialties keep patient data confidential and share them only when needed. The necessary conditions would be for the patient’s treatment, payment reasons or other healthcare reasons.
The law provides rights to patients to access their information and correct their records whenever necessary. HIPAA imposes non–compliance penalties to those who are non-compliant to prevent data breaches and misuse of patient data.
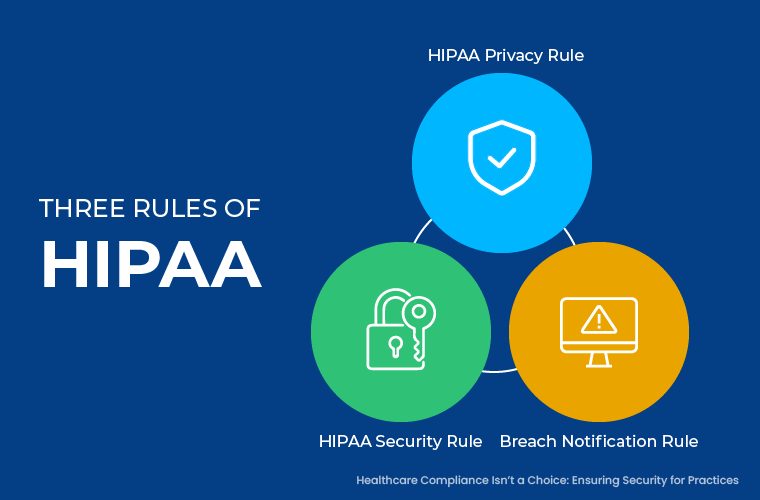
With HIPAA privacy rule, there are key provisions such as:
- Privacy Rule – To protect patient health information (PHI)
- Security Rule – To protect electronic PHI (ePHI)
- Breach Notification Rule – Covered entities to help affected individuals, and the OCR to address in the event of a data breach.
HIPPA applies to three types of safeguards to the security rule including:
- Technical Safeguards – Utilizing technical solutions like firewalls or encryption tools to prevent data breaches or ePHI disclosure. Examples like monitoring system, audit controls, and more.
- Administrative Safeguards – Programs like risks assessments, training sessions, and more taken in a healthcare organization to protect ePHI.
- Physical Safeguards – Restricting the physical access to locations inside facilities where ePHI is stored and protected. These may be workstation security controls, access controls, etc.
Penalties for Non-Compliance HIPAA:
HIPAA outlines several non-compliance penalties for those who are non-compliant and violating the rules. The penalties for non-compliance HIPAA are of four different levels.
Civil Penalties:
Level 1: Lack of awareness – It carries a HIPAA violation fines of $100 to $50K per violation, and sometimes maximum of up to $1.5 million per year.
Level 2: Lack of Due Diligence – It results in a HIPAA Violation fines of amount of $1,000 to $50,000 per violation.
Level 3: Willfully Default and Neglect taking effort to correct – It incurs a fine amount of $10,000 to $50,000 per violation.
Level 4: Willfully Neglect without taking corrective action – It carries a penalty of 50,000 per violation, of up to $1.5 million per year.
What is HITRUST?

HITRUST stands for the Health Information Trust Alliance. It is a certifiable framework helping healthcare organizations manage compliance and risks in protecting sensitive data. The main reason behind its development is to create and follow a standardized approach for security information alongside aligning with HIPAA, GDPR regulations.
It provides a scalable framework for practices to follow the best methods in protecting your patient’s data. Furthermore, with HITRUST certification, practices can meet stringent security requirements and ensure assurance of safeguarding protected health information (PHI).
When an organization achieves HITRUST certification, it is easy for them to satisfy 40 more compliance frameworks. Some of them including:
- HIPAA compliance
- SOC 2
- FedRAMP
- GDPR
- CCPA
- PCI DSS
ISO 27001 and NIST 800-53
HITRUST certification is particularly important for practices because:
- It eases the tasks of managing multiple compliance frameworks like HIPAA, GDPR, etc.
- It sets a standardized approach to data protection.
- It improves your confidence in protecting your patient’s sensitive information.
What is SOC 2 Type II?

SOC 2 stands for System and Organization Controls. The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) developed this framework that comes under one of five sets of standards. With this standard, healthcare practices can easily evaluate that their security, privacy and admin processes are enough.
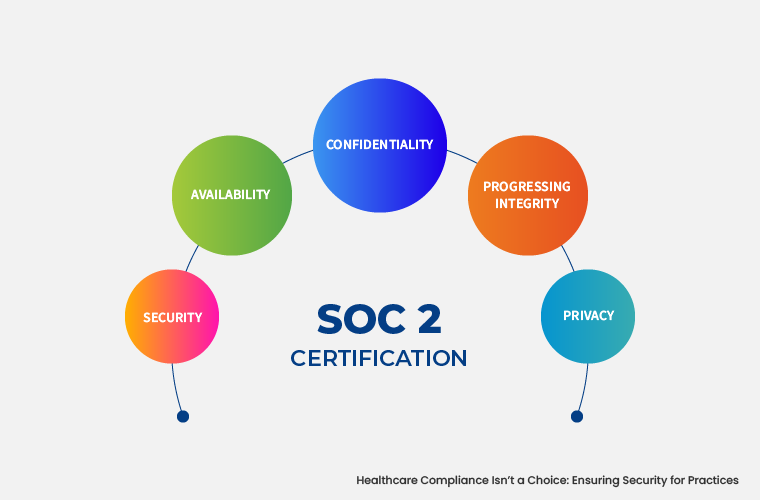
SOC 2 compliance is significant for C-suite, business partners handling sensitive customer information. It is relevant to healthcare, as its framework aligns closely with HIPAA requirements. The SOC 2 controls have five Trust Services Criteria including:
- Security
- Availability
- Processing Integrity
- Privacy
- Confidentiality
Importance of SOC 2 Type 2 Compliance for Healthcare:
SOC 2 Type II compliance is particularly important as it demonstrates to patients that the systems and processes involved in your practices are safe and reliable. With this, all the patient data is completely protected following the set standards and regulations.
Hence, it is evident for healthcare providers to have SOC 2 Type 2 compliance for
- Protection against data breaches using a robust framework to improve your brand reputation using security controls and processes
- Maintaining a competitive differentiation to showcase others that you are committed to protecting patient’s sensitive data
- Streamline internal process to address everyone in your organization to understand their roles and responsibilities in data security
What is GDPR Compliance?

GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), a comprehensive data protection law developed by the European Union (EU) in May 2018. In addition to safeguarding PHI (Protected Health Information), GDPR regulates personally identifiable information (PII).
GDPR gives EU citizens the various rights to access and change their information. Some of them include:
- Right to rectify records
- Right to access personal information
- Right to delete records
- Right to restrict data processing
- Right to data portability
Why GDPR Compliance Matters in US Healthcare?
How does it matter for the US healthcare practices to be compliant with GDPR? Yes, it looks unrelated, but it plays a vital role in cross-border patient data processing. GDPR ensures that your healthcare practices follow stringent security measures and maintains consistent protection standards for patient information.
For U.S healthcare practices, GDPR compliance is not only important but essential as well. Here is how GDPR non-compliance can affect your independent medical practice or an organization.
- Globalization of Cross-Border Data – Under GDPR, any healthcare practices should comply with its security standards to process or use the personal or health information of EU citizens.
- Telehealth – If a U.S based telemedicine provider is handling data from an EU citizen, they must stick to GDPR standards, otherwise they will face GDPR non-compliance fine.
- GDPR Non-compliance Penalties – Though U.S healthcare providers may not come under EU jurisdiction, they will end up with penalties for failing to meet the standards, when handling EU citizen’s data.
- Security Standards – Eliminate the risks of data breaches and cyberattacks with GDPR compliance, protecting patient information and avoiding the reputational and financial fallout that often follows a security breach.
GDPR Penalties
- GDPR non-compliance fines may incur up to €10 million or 2% of the worldwide annual revenue, whichever is higher, for less severe violations.
- Up to €20 million or 4% of the worldwide annual revenue, whichever is higher, for more severe violations.
Well, we had a detailed overview of all those compliances that are the utmost important for any healthcare practices.
Now, let us brief you on the things that how integrating with CERTIFY Health helps you achieve and maintain these important regulations.
What is PCI DSS Compliance?
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a global security standard for protecting cardholder data and authentication information. It applies to all sectors, including the healthcare sector, if they accept payment cards.
PCI DSS compliance requires healthcare providers to securely handle card data, store it with security, and validate compliance annually by methods like Self-Assessment Questionnaires or third-party audits.
Key Components of PCI DSS Compliance
- Handling Card Data: Healthcare providers should collect and transmit sensitive card details securely.
- Storing Data Securely: Leverage robust security measures like encryption and monitoring for secure storage.
- Validate Compliance: Healthcare providers must validate compliance through forms, audits, and vulnerability scans.
PCI DSS Non-Compliance Fines:
- PCI DSS non-compliance fines can range between $5000 and $100,000 per month, depending on the severity and duration of the non-compliance.
- Banks or Payment Processors determine the exact cost of penalties, and if not addressed promptly, the amount escalates over time.
- Non-compliance also results in potential lawsuits, monthly fines, and bans or listing on the Terminated Merchant File (TMF).
Why Integrating with CERTIFY Health Guarantees Seamless Compliance?
Meet all Healthcare Compliance Regulations:
Ensuring all Security Features
Our platform utilizes advanced security features such as FaceCheck (PPID), data encryption, and regular risk assessments to eliminate data breaches and to protect the sensitive patient’ data. As we implement all these security measures and stringent methods, practices can significantly reduce their risk of data breaches and ransomware attacks, building patient trust and loyalty.
Maintaining Streamlined Workflows
Driving Patient-Centric Approach
Conclusion: The Imperative of Prioritizing Security Healthcare Compliance
By partnering with CERTIFY Health, we can help your healthcare practice implement robust security compliance measures that align with HIPAA, HITRUST, GDPR, and SOC 2 Type II standards. With our comprehensive solutions and expert guidance, we’re committed to ensuring that your patient data is secure, allowing you to focus on what you do best—delivering quality care.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, I believe prioritizing security compliance isn’t just a best practice—it’s an absolute necessity. When you choose CERTIFY Health as your trusted partner, we’ll work together to achieve compliance and protect the valuable data of your patients. Let’s navigate the complexities of healthcare security together and build a safer, more secure future for all. – Book a Demo!
FAQs
What are HIPAA penalties for non-compliance?
Who sets HIPAA fines and penalties?
What is the difference between HIPAA and HITRUST?
What is the purpose of HITRUST?
What are the pillars of SOC 2?
The five SOC 2 trust principles are:
- Security
- Availability
- Processing Integrity
- Confidentiality
- Privacy











